Simultaneous screening for lung cancer and coronary atherosclerosis in the military, firefighters and civilians of Ukraine during and after the war
According to Global Health data, for every death in war, there may be nine deaths that are not related to combat operations at first glance.
It is known that over the past 20 years, the number of certain types of cancer in US army veterans has increased by 110%. Former military personnel are at risk of developing malignant tumors of the liver, pancreas, bladder, kidneys, ureters, prostate, melanoma, thyroid, brain tumors, lymphoma and leukemia.
Female military personnel and volunteers are almost 40% more likely to develop breast cancer than the rest of the population.
It is also known that army veterans have a significantly increased risk of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Thus, after the Korean War, 80% of men under the age of 35 had coronary artery disease, and after the Vietnam War, it was found that atherosclerosis was present in 45% of combatants, and in 5% of cases the disease was severe.
Today, convincing evidence has been obtained that atherosclerosis and cancer develop simultaneously.
Therefore, military personnel and firefighters are at increased oncological and cardiological risk. In the near future, after the war, lung cancer and coronary heart disease may become the main problem for the military and civilian population of Ukraine.
All this requires measures for primary and secondary prevention of cancer and atherosclerosis.
At the initiative and support of the World Against Cancer Foundation, a program of preventive and therapeutic cardio-oncology was developed and launched, which included, among other things, simultaneous screening for lung cancer and coronary atherosclerosis in risk groups. The Foundation contributed to and financed the publication of a manual for family doctors, oncologists and cardiologists.
It is known that over the past 20 years, the number of certain types of cancer in US army veterans has increased by 110%. Former military personnel are at risk of developing malignant tumors of the liver, pancreas, bladder, kidneys, ureters, prostate, melanoma, thyroid, brain tumors, lymphoma and leukemia.
Female military personnel and volunteers are almost 40% more likely to develop breast cancer than the rest of the population.
It is also known that army veterans have a significantly increased risk of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Thus, after the Korean War, 80% of men under the age of 35 had coronary artery disease, and after the Vietnam War, it was found that atherosclerosis was present in 45% of combatants, and in 5% of cases the disease was severe.
Today, convincing evidence has been obtained that atherosclerosis and cancer develop simultaneously.
Therefore, military personnel and firefighters are at increased oncological and cardiological risk. In the near future, after the war, lung cancer and coronary heart disease may become the main problem for the military and civilian population of Ukraine.
All this requires measures for primary and secondary prevention of cancer and atherosclerosis.
At the initiative and support of the World Against Cancer Foundation, a program of preventive and therapeutic cardio-oncology was developed and launched, which included, among other things, simultaneous screening for lung cancer and coronary atherosclerosis in risk groups. The Foundation contributed to and financed the publication of a manual for family doctors, oncologists and cardiologists.

The screening examination includes performing low-dose computed tomography of the lungs (LDCT) and measuring the content of calcium salts in the coronary arteries using non-contrast multidetector computed tomography of the heart (MDCT). The degree of arterial calcification is quantified using the Agatston scale.
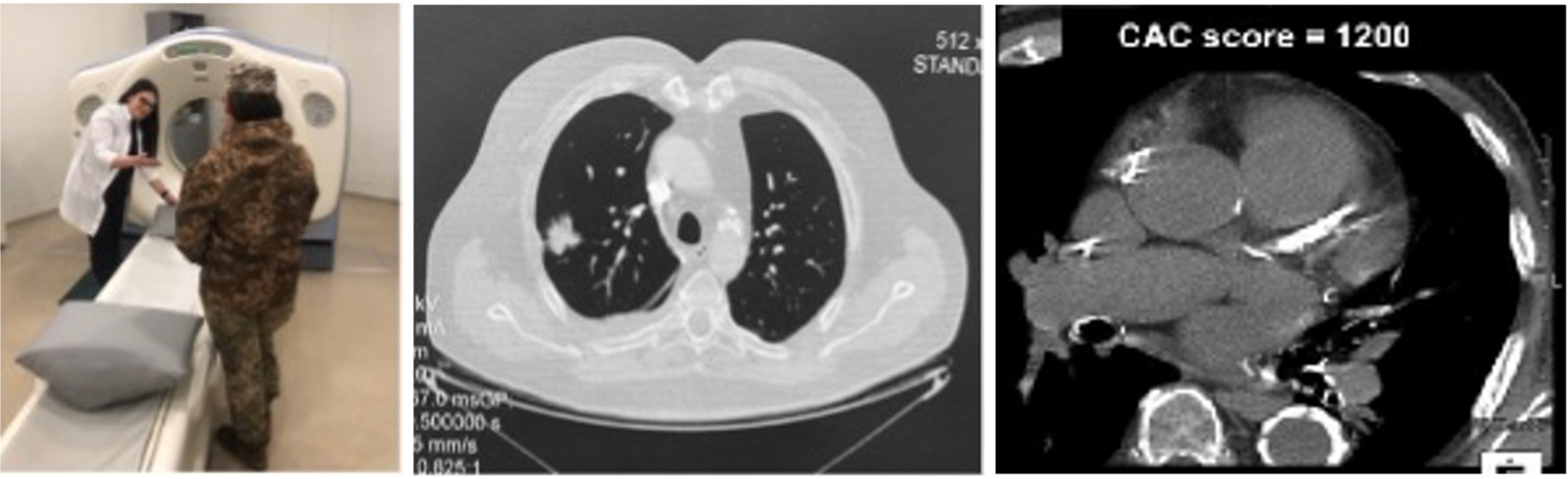
The first results were reported in August 2024 at the World Cancer Congress in Geneva, Switzerland, which was held under the auspices of the International Union Against Cancer (UICC).
This Ukrainian innovative project from the city of Zaporizhzhia was approved by the EU scientific community.
This Ukrainian innovative project from the city of Zaporizhzhia was approved by the EU scientific community.
